Breast Anatomy
The breasts of an adult woman are milk-producing, tear-shaped glands. They are supported by and attached to the front of the chest wall on either side of the breast bone or sternum by ligaments. They rest on the major chest muscle, the pectoralis major.
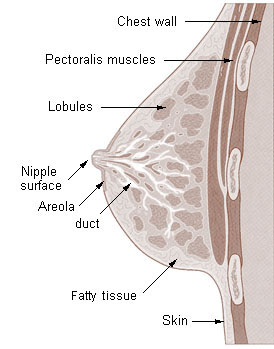
The breast has no muscle tissue. A layer of fat surrounds the glands and extends throughout the breast.
The breast is responsive to a complex interplay of hormones that cause the tissue to develop, enlarge and produce milk. The three major hormones affecting the breast are estrogen, progesterone and prolactin, which cause glandular tissue in the breast and the uterus to change during the menstrual cycle.
Each breast contains 15 to 20 lobes arranged in a circular fashion. The fat (subcutaneous adipose tissue) that covers the lobes gives the breast its size and shape. Each lobe is comprised of many lobules, at the end of which are tiny bulb like glands, or sacs, where milk is produced in response to hormonal signals.
Ducts connect the lobes, lobules, and glands in nursing mothers. These ducts deliver milk to openings in the nipple. The areola is the darker-pigmented area around the nipple.
