Layers of UGI Organs
Layers of Esophageal Wall
The esophageal wall contains four layers:
- mucosa—surface epithelium, lamina propria, and glands
- submucosa—connective tissue, blood vessels, and glands
- muscularis (middle layer)
- upper third, striated muscle
- middle third, striated and smooth
- lower third, smooth muscle
- adventitia—connective tissue that merges with connective tissue of surrounding structures
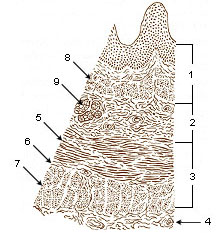
- Mucosa
- Submucosa
- Muscularis
- Adventitia
- Striated muscle
- Striated and smooth
- Smooth muscle
- Lamina muscularis mucosae
- Esophageal glands
Layers of Stomach Wall
Layers of the stomach wall, among others, include serosa, muscularis, submucosa, mucosa. The three layers of smooth muscle consist of the outer longitudinal, the middle circular, and the inner oblique muscles. Construction of these muscles helps mix and break the contents into a suspension of nutrients called chyme and propels it into the duodenum.
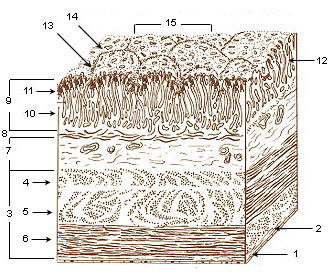
- Serosa
- Tela subserosa
- Muscularis
- Oblique fibers of muscle wall
- Circular muscle layer
- Longitudinal muscle layer
- Submucosa
- Lamina muscularis Mucosae
- Mucosa
- Lamina propria
- Epithelium
- Gastric glands
- Gastric pits
- Villous folds
- Gastric areas (gastric surface)
Suggested Citation
SEER Training Modules: Layers of UGI Organs. U.S. National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute. Cited 02 March 2026. Available from: https://training.seer.cancer.gov.




