Staging
The traditional staging for Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma was initially presented at the Ann Arbor Symposium on Staging of Hodgkin lymphoma, April, 1971. For the Ann Arbor System, clinical staging includes all of the non-invasive procedures; pathologic staging is based on findings made as a result of invasive procedures such as laparotomy or mediastinotomy.
Definitions for TNM clinical staging and pathologic staging using the Ann Arbor system are the same. T, N, and M elements are not applicable to this staging system.
Criteria for TNM Clinical Staging: Physical examination and history; urinalysis; chest x-ray; blood chemistries; bilateral bone marrow biopsies, plus lymphangiogram, abdominal CT scan. Also (optional, depending on previous findings) bone imaging, technetium scans, CT scans, chest tomography, upper GI series, lumbar puncture, ultrasound, gallium scans, liver/spleen scan.
Criteria for TNM Pathologic Staging: All of the clinical studies above, plus biopsy of accessible extranodal primary site(s). Staging laparotomy (including splenectomy, wedge liver biopsy, and multiple lymph node biopsies) is not required but may be used for additional staging information if indicated. Otherwise, liver biopsy, or other biopsies to determine distant metastases.
The Cotswolds Modifications of the Ann Arbor Staging Classification
- Add a suffix X to designate bulky disease (defined as a mass of nodes with one diameter of > 10 cm or a mediastinal mass of > 1/3 of the transthoracic {mediastinal} width)
- The number of anatomic regions involved should be indicated by a subscript (e.g., II3)
- Stage III may be subdivided into:
- III1 with or without splenic, hilar, celiac, or portal nodes
- III2 with para-aortic, iliac, or mesenteric nodes
- Staging should be identified as clinical stage (CS) or pathologic stage (PS)
- A new category of response to therapy, unconfirmed/uncertain complete remission, should be introduced because of the persistent radiologic abnormalities of uncertain significance
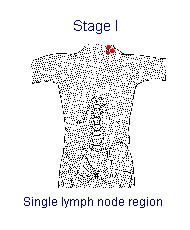
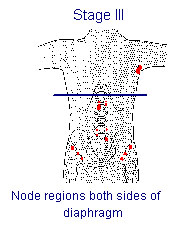
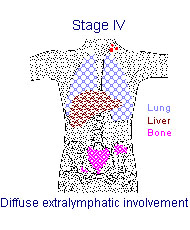
Ann Arbor Staging (AJCC Stage Groups)
 |
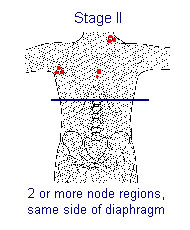 |
| Stage I also: single extranodal organ (Ie) | Stage II also: single extranodal organ plus its regional lymph nodes with or without other nodes on same side of diaphragm (IIe) |
 |
 |
| Stage III also: localized involvement of extralymphatic organ or site plus nodes on both sides of diaphragm (IIIe) OR involved lymph nodes on both sides of diaphragm plus spleen (IIIs) |
Hodgkin Lymphoma and Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas
Relationship of Staging Systems
| Description of Extent (based on Ann Arbor definitions) |
Summary Stage | Ann Arbor Staging * | AJCC Staging Stage† |
|---|---|---|---|
| Involvement of a single lymph node region | Localized | I | I |
| A single extralymphatic organ or site | Localized | Ie | Ie |
| Involvement of more than one lymphatic region on only one side of the diaphragm | Regional, NOS | II | II |
| Localized involvement of one extralymphatic organ or site and its regional lymph nodes with or without other nodes on the same side of the diaphragm | Regional, NOS | IIe | IIe |
| Involvement of more than one lymphatic region on only one side of the diaphragm plus involvement of the spleen | Distant | IIs | IIs |
| Involvement of lymph node regions on both sides of the diaphragm | Distant | III | III |
| Involvement of lymph node regions on both sides of the diaphragm plus localized involvement of an extralymphatic organ or site | Distant | IIIe | III |
| Involvement of lymph node regions on both sides of the diaphragm plus involvement of the spleen | Distant | IIIs | IIIs |
| Diffuse or disseminated involvement of one or more extralymphatic organs or tissues with or without associated lymph node enlargement. Organs considered distant include liver, bone, bone marrow, lung and/or pleura, and kidney. | Distant | IV | IV |
| Isolated extralymphatic organ involvement with distant (non-regional) nodal involvement | Distant | IV | IV |
Collaborative Stage Elements
For more details on Collaborative Stage, see the Intro to Collaborative Staging module.
