Mouth
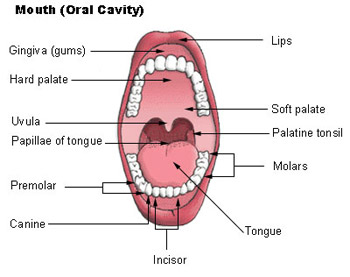
The mouth, or oral cavity, is the first part of the digestive tract. It is adapted to receive food by ingestion, break it into small particles by mastication, and mix it with saliva. The lips, cheeks, and palate form the boundaries. The oral cavity contains the teeth and tongue and receives the secretions from the salivary glands.
Lips and Cheeks
The lips and cheeks help hold food in the mouth and keep it in place for chewing. They are also used in the formation of words for speech. The lips contain numerous sensory receptors that are useful for judging the temperature and texture of foods.
Palate
The palate is the roof of the oral cavity. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. The anterior portion, the hard palate, is supported by bone. The posterior portion, the soft palate, is skeletal muscle and connective tissue. Posteriorly, the soft palate ends in a projection called the uvula. During swallowing, the soft palate and uvula move upward to direct food away from the nasal cavity and into the oropharynx.
Tongue
The tongue manipulates food in the mouth and is used in speech. The surface is covered with papillae that provide friction and contain the taste buds.
Teeth
A complete set of deciduous (primary) teeth contains 20 teeth. There are 32 teeth in a complete permanent (secondary) set. The shape of each tooth type corresponds to the way it handles food.
Suggested Citation
SEER Training Modules: Mouth. U.S. National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute. Cited 09 March 2026. Available from: https://training.seer.cancer.gov.




