Classification of Bones
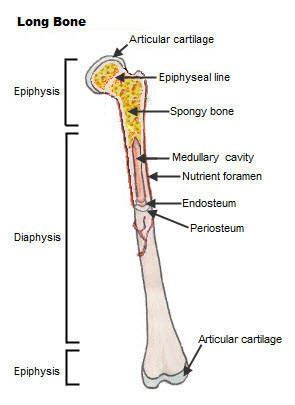
Long Bones
The bones of the body come in a variety of sizes and shapes. The four principal types of bones are long, short, flat and irregular. Bones that are longer than they are wide are called long bones. They consist of a long shaft with two bulky ends or extremities. They are primarily compact bone but may have a large amount of spongy bone at the ends or extremities. Long bones include bones of the thigh, leg, arm, and forearm.
Short Bones
Short bones are roughly cube shaped with vertical and horizontal dimensions approximately equal. They consist primarily of spongy bone, which is covered by a thin layer of compact bone. Short bones include the bones of the wrist and ankle.
Flat Bones
Flat bones are thin, flattened, and usually curved. Most of the bones of the cranium are flat bones.
Irregular Bones
Bones that are not in any of the above three categories are classified as irregular bones. They are primarily spongy bone that is covered with a thin layer of compact bone. The vertebrae and some of the bones in the skull are irregular bones.
All bones have surface markings and characteristics that make a specific bone unique. There are holes, depressions, smooth facets, lines, projections and other markings. These usually represent passageways for vessels and nerves, points of articulation with other bones or points of attachment for tendons and ligaments.
Suggested Citation
SEER Training Modules: Classification of Bones. U.S. National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute. Cited 01 March 2026. Available from: https://training.seer.cancer.gov.




