Nose, Nasal Cavities, & Paranasal Sinuses
Nose & Nasal Cavities
The framework of the nose consists of bone and cartilage. Two small nasal bones and extensions of the maxillae form the bridge of the nose, which is the bony portion. The remainder of the framework is cartilage and is the flexible portion. Connective tissue and skin cover the framework.
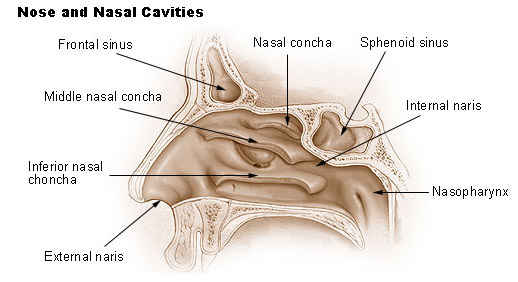
Air enters the nasal cavity from the outside through two openings: the nostrils or external nares. The openings from the nasal cavity into the pharynx are the internal nares. Nose hairs at the entrance to the nose trap large inhaled particles.
Paranasal Sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are air-filled cavities in the frontal, maxilae, ethmoid, and sphenoid bones. These sinuses, which have the same names as the bones in which they are located, surround the nasal cavity and open into it. They function to reduce the weight of the skull, to produce mucus, and to influence voice quality by acting as resonating chambers.
Suggested Citation
SEER Training Modules: Nose, Nasal Cavities, & Paranasal Sinuses. U.S. National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute. Cited 09 March 2026. Available from: https://training.seer.cancer.gov.




